Raymii.org

אֶשָּׂא עֵינַי אֶל־הֶהָרִים מֵאַיִן יָבֹא עֶזְרִֽי׃Home | About | All pages | Cluster Status | RSS Feed
Embed the source code directly in your Qt app with qmake and qrc, for GPL compliance
Published: 12-02-2022 | Author: Remy van Elst | Text only version of this article
❗ This post is over three years old. It may no longer be up to date. Opinions may have changed.
Table of Contents
In my earlier post on selling GPL software I outlined a few points that make it hard to sell GPL software. One of them is the availability of the source code. You could put it online but then everyone has access without paying. Other options like putting it behind a login or sending a link after purchase require extra systems and saving more user information, lots of extra hassle for me and the users.
One of my ideas for 'solving' this issue is by shipping the actual source code directly inside the application. This article shows you how to do that, by creating an archive of the current source code on every build with qmake and embedding that inside the application using qrc, including a button to save the archive locally to disk. It works on the desktop as well as Android, including the required permissions.
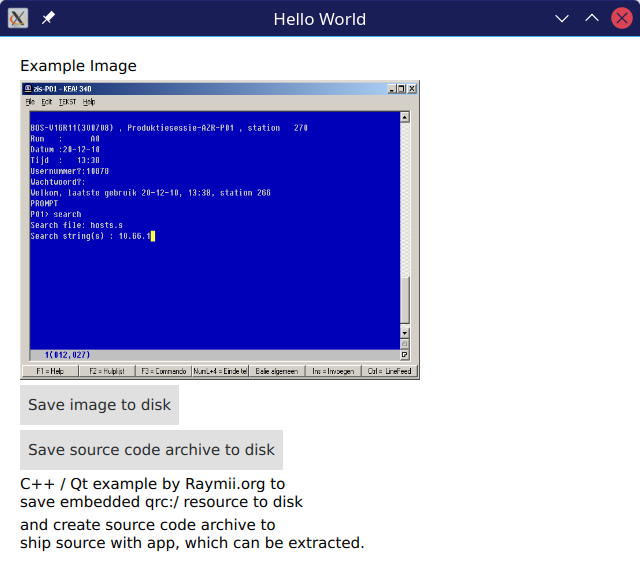
Screenshot of the demo application
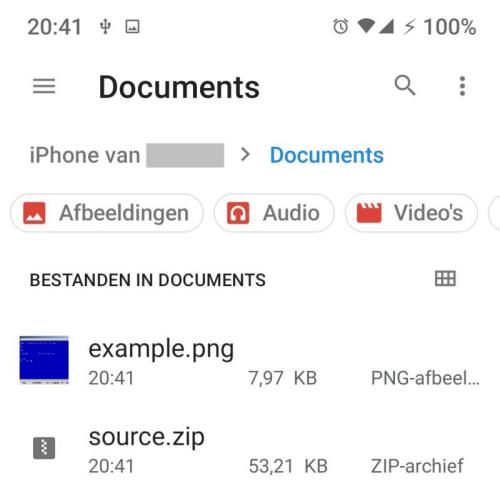
The example program has 2 buttons, one to save the zip archive we dynamically create on every build and one to save the example image. The example image is a random screenshot I found in an old folder from one of my previous jobs, that system is no longer in use.
This solves another hurdle, the mobile app source aspect. On a desktop
I can provide a zip file with the installer and source code, but in the
app stores I cannot do that, just an .apk file or .aab bundle.
By embedding the code inside the application, on Android the users can save the code from within the app to their system, no need to download a source archive.
This guide works for Qt5 and assumes you're familiar with the Qt framework and Qml. The demo program can be found on github. The first part of the guide covers dynamically creating the source archive on every build and the second part covers embedding it in a Qt application.
This is part 2 in my series on selling GPL software. You can find the other parts here:
- Part 1: Selling my own GPL software, part 1: a lot of hurdles
- Part 2: Embed the source code directly in your Qt app with qmake and qrc, for GPL compliance
- Part 3: Existing GPL software for sale
Source code availability
If you haven't read the previous article, I recomend you do, as this explains why I'm struggling with this part, source code availability. I do want the source to be available, but only to actual customers. Whatever they then do with the source code is their right, as long as it's compliant with the GPL. So I'm not against publishing the code, but I also don't want to end up with the software being available everywhere. In the end, if a customer does buy the program and publishes the source, it's their right to do so and I'm fine with that.
The GPL FAQ has three Q&A items regarding charging and source distribution which answer all the questions you might have:
Does the GPL allow me to sell copies of the program for money?
Yes, the GPL allows everyone to do this. The right to sell copies is part of the definition of free software. Except in one special situation, there is no limit on what price you can charge. (The one exception is the required written offer to provide source code that must accompany binary-only release.)
Does the GPL allow me to charge a fee for downloading the program from my distribution site?
Yes. You can charge any fee you wish for distributing a copy of the program. Under GPLv2, if you distribute binaries by download, you must provide "equivalent access" to download the source--therefore, the fee to download source may not be greater than the fee to download the binary. If the binaries being distributed are licensed under the GPLv3, then you must offer equivalent access to the source code in the same way through the same place at no further charge.
If I distribute GPLed software for a fee, am I required to also make it available to the public without a charge?
No. However, if someone pays your fee and gets a copy, the GPL gives them the freedom to release it to the public, with or without a fee. For example, someone could pay your fee, and then put her copy on a web site for the general public.
The last line of the second item, you must offer equivalent access to the
source code in the same way through the same place at no further charge,
seems to be covered as far as I can tell when I provide the source together
with the download and inside the application (whenever a download is not
possible such as on app-stores).
One of the effects of this way of publishing the source code is that you do need to be able to run the application before you can extract the source code. Newer versions also require a new purchase, since the app only ships with that version's source code. On desktop platforms I do plan to ship an archive of the source in the download after purchase, so you're not required to run the application to get the source, but on Android in the app store that is not possible. So, in that case, this is best effort, if it even gets through app-store review.
qmake a source code archive
You can find the example project here on github. This section
of the article covers how the source code archive is made, later on we'll
cover the qrc section to extract the archive on disk.
I'm shipping a simple .zip archive with the source code and relevant
project files. The file is created with the following command:
zip -r source.zip ./ -i '*.cpp' '*.h' '*.qml' '*.qrc' '*.pro' '*.png' 'README.md' 'LICENSE'
This command produces a zip file relative to the current working directory
in which the folder structure is preserved. It includes all files on
the wildcard extensions list and the README.md file.
This file, source.zip, is referenced in the DISTFILES section of the .pro
file as well as in the qrc file (to be embedded in the application), so
it must be available before building the program.
At first I tried to add an extra compiler to the qmake project file,
as is documented here, but that was a bit of a hassle. Either I
had to add all input files, otherwise changes would not be detected,
or there would be a lot of variable trickery. Also, when the command
runs wasn't entirely predictable, and I need to run the command before
the actual build. This is because we reference the source.zip file in
our qrc file, it must be there before we build.
In the end I used a simple system() command, which is guaranteed to run
before the actual build:
system(cd $$PWD; rm source.zip; zip -r source.zip ./ -i \'*.cpp\' \'*.h\' \'*.qml\' \'*.qrc\' \'*.pro\' \'*.png\' \'android/*\' 'README.md' 'LICENSE')
This is not cross-platform and only works with this specific zip version's commandline flags, but for now that's fine enough. I can always encapsulate a different command later on in a block like below:
win32 {
system(windows command)
} else {
system(linux command)
}
The output when building via Qt Creator or running qmake looks like this:
19:48:23: Running steps for project qrcToDisk...
19:48:23: Starting: "/bin/qmake" /src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/qrcToDisk.pro -spec linux-g++ CONFIG+=debug CONFIG+=qml_debug
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/files/example.png (deflated 14%)
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/SaveToDisk.cpp (deflated 56%)
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/qml.qrc (deflated 36%)
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/main.qml (deflated 64%)
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/main.cpp (deflated 50%)
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/qrcToDisk.pro (deflated 41%)
adding: src/QtExamples/qrcToDisk/SaveToDisk.h (deflated 33%)
19:48:23: The process "/bin/qmake" exited normally.
If you omit the rm command, any already existing files will be overwritten and new files
are added. Old files are not removed.
The zip archive opens just fine and the contents are as expected:
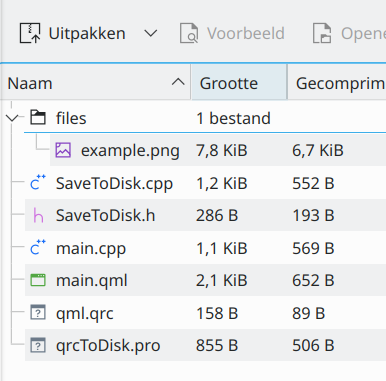
Save a Qt qrc embedded file to disk
A qrc file is part of the Qt resource system. The Qt resource system is
a platform-independent mechanism for storing binary files in the
application's executable. Most often qmake generates make rules to
generate the file qrc_application.cpp which is linked into your
application. This file contains all the data for the images and other
resources as static C++ arrays of compressed binary data.
You can also configure qrc to create an external binary resource file which
is later registered with the resource system. This is useful if you have, for
example, two sets of images for the same codebase.
Below you'll find the example contents of my qml.qrc file:
<RCC>
<qresource prefix="/">
<file>main.qml</file>
<file>files/example.png</file>
<file>source.zip</file>
</qresource>
</RCC>
Copying a file out of qrc to the filesystem is as simple as calling
QFile::copy. QFile supports the Qt resource system and if your file's
path starts with a colon (:), it knows to look in the resource system
for the filename. An example:
QFile::copy(":/files/example.png", "/tmp/example.png");
With the above qrc file, the file example.png that is embedded in the
application will be copied to the /tmp folder.
The demo program I wrote to test this does a bit more, like sanitizing the
filename, checking for non-existing folders and overwriting, but the one
QFile::copy like is the gist of it.
One problem I had was that at first I used a QML FileDialog to let the
user select the folder to save the files into. The returned path however, on
linux, started with file://, instead of just the path(/home/user/...). On
Android, the path returned, no matter what the user choose, was
/data/user/0/org.qtproject.example.qrcToDisk, which is not a folder the
user can browse to. At first I tried to work around those issues, but that
proved not to work reliably, so I opted to just use
QStandardPaths::DocumentsLocation, which should always return something,
create the folder if needed.
One other thing to keep in mind is that by default the permissions of files
in the qrc file are read-only (since you can't write back to it) and
QFile copies those permissions. In the example project I set the file
permission of the new file to be writable.
Same thing goes for the case where the destination file already exists,
QFile::copy will fail unless you manually remove that file.
In this example I overwrite any existing files, it's up to any users of this example to implement a user question to overwrite.
There is a bit of boilerplate code to request permissions dynamically on
Android, those permissions are already in the AndroidManifest.xml file,
but newer versions of Android also require you to ask for them before
using them, so we do. If it all works, it looks like below:
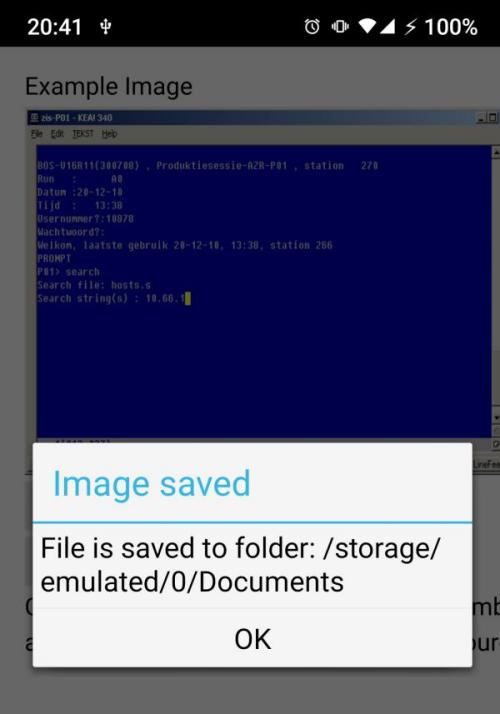
Once saved, the files are in the Documents folder: